Importance of Healthy Eating for Kids
Healthy eating forms the foundation for a child’s growth, development, and overall well-being. Balanced diets provide essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins necessary for bodily functions and cognitive development.
Research from the CDC shows that proper nutrition helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains strengthens the immune system, making children less prone to infections.
Moreover, balanced nutrition supports mental health. Studies indicate that children who consume nutrient-dense meals exhibit better concentration, improved mood, and higher academic performance than those with poor diets. Healthy eating habits established in childhood often persist into adulthood, reducing long-term health risks.
Instilling these habits early ensures children understand the value of nutritious foods over processed options. By incorporating diverse, colorful ingredients into meals, parents can make healthy foods appealing to kids, promoting lifelong healthy eating habits.
Overview of New Nutritional Guidelines
New nutritional guidelines help parents navigate the complexities of healthy eating for kids. Understanding these changes ensures children get the nutrients they need for growth and development.
Key Changes in Nutritional Recommendations
The latest guidelines emphasize more plant-based foods. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes reduces the risk of chronic diseases. The recommendations now limit added sugars to less than 10% of daily calories for kids over 2 years. Saturated fats should make up less than 10% of their daily calories, while sodium intake should not exceed 1,500 mg per day for children aged 4 to 8. These changes aim to support better long-term health outcomes.
Age-Specific Nutritional Needs
Kids’ nutritional needs vary by age. For children aged 1-3, focus on nutrient-dense foods, offering small, frequent meals. From 4-8 years, balance macronutrient intake with a diverse mix of proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy. Children aged 9-13 need more iron and calcium as they enter puberty. Understanding age-specific requirements ensures proper support for each developmental stage.
Recommended Daily Intake of Essential Nutrients
Accurately tracking nutrient intake ensures balanced diets. Here’s a snapshot of daily recommendations:
| Nutrient | 1-3 years | 4-8 years | 9-13 years |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 13g | 19g | 34g |
| Calcium | 700mg | 1,000mg | 1,300mg |
| Iron | 7mg | 10mg | 8mg |
| Fiber | 19g | 25g | 26g (girls), 31g (boys) |
| Vitamin D | 600 IU | 600 IU | 600 IU |
Balanced diets, based on these guidelines, optimize growth and promote lifelong health habits.
Implementing the Guidelines at Home

It’s crucial to integrate new nutritional guidelines into daily routines to ensure children get balanced diets. This involves thoughtful meal planning, choosing healthy snacks, and encouraging picky eaters.
Meal Planning and Preparation Tips
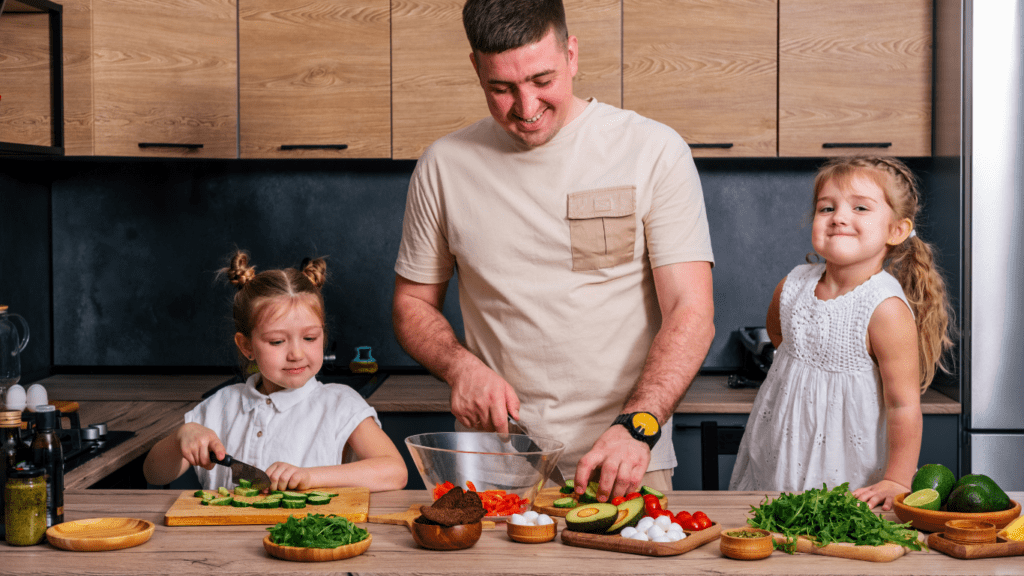
Menu planning simplifies healthy eating. I start by including a variety of food groups in each meal. Breakfast could feature whole grains, fruits, and dairy. For lunch, consider lean proteins and vegetables. Dinner might include a mix of carbs, proteins, and fats. Mixing up the menu can reduce dietary monotony.
Portion control plays a key role. Using smaller plates for younger kids helps regulate portion sizes and prevents overeating. Engaging kids in meal preparation can make them more interested in what they eat. They might enjoy washing vegetables or helping to mix ingredients.
Batch cooking saves time and ensures availability of healthy options. I often prepare large quantities of soups, stews, or roasted vegetables and freeze them in portioned containers. This method ensures quick, nutritious meals are always on hand.
Healthy Snack Alternatives
Snacks significantly impact nutrition, so choosing healthy options is essential. I opt for fresh fruits, vegetables with hummus, or yogurt instead of processed snacks. Whole-grain crackers with cheese also offer a balance of carbs and proteins.
For homemade options, energy balls made from oats, nut butter, and dried fruits, or homemade popcorn seasoned lightly, serve as excellent choices. Smoothies with spinach, fruits, and greek yogurt are both tasty and nutrient-dense.
Reducing sugar intake can improve health outcomes. Instead of sugary snacks, I offer naturally sweetened options like fruits or snacks made with honey or maple syrup.
Encouraging Picky Eaters
Picky eating presents a common challenge. Introducing new foods gradually can help. I usually serve new items alongside favorites to increase acceptance. Maintaining a positive mealtime atmosphere encourages kids to try different foods without pressure.
Healthy eating games make food discovery fun. Engagement activities like a “taste test” game where children rate new foods can be effective. Rewarding small tries with stickers or verbal praise helps build positive associations with food.
Modeling behavior works wonders. When children see adults enjoying healthy foods, they’re more likely to try them. Preparing and eating meals together strengthens this influence.
Role of Schools and Community
Schools and communities play a crucial role in promoting healthy eating habits among kids. They reinforce what children learn at home and provide additional support for balanced diets.
Nutritional Programs in Schools
Schools implement various nutritional programs to ensure kids receive healthy meals. Many schools now offer:
- School Breakfast and Lunch Programs: Schools provide balanced meals that meet dietary guidelines. They include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Farm-to-School Initiatives: Schools partner with local farms to supply fresh produce. These programs expose children to fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Nutrition Education: Curriculum includes lessons on healthy eating. Kids learn about portion sizes, food groups, and the importance of a balanced diet.
- Healthy Vending Options: Schools replace sugary snacks with healthier alternatives. Options include nuts, seeds, and fresh fruit.
Community Resources and Support
Communities offer various resources to assist parents and kids in maintaining healthy eating habits. These resources often include:
- Local Food Banks: Food banks provide access to nutritious foods. They distribute fresh produce, dairy, and protein items to families in need.
- Community Gardens: Gardens encourage families to grow their own vegetables. They provide a space for learning and access to fresh produce.
- Nutrition Workshops: Workshops educate families on healthy eating. They cover meal planning, grocery shopping, and cooking nutritious meals.
- Recreational Programs: Programs promote physical activity and healthy lifestyles. They include sports, fitness classes, and family wellness activities.
Schools and community programs collectively foster an environment that encourages kids to adopt and maintain healthy eating habits.
Benefits of Adopting the New Guidelines
Adopting the new nutritional guidelines provides several benefits for kids. It ensures they grow up healthy and develop lifelong good eating habits.
Improved Physical Health
Children’s physical health gains much when parents follow updated nutritional guidelines. Balanced diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains help maintain a healthy weight and support growth. Limiting added sugars and saturated fats reduces the risk of childhood obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Additionally, adequate nutrient intake strengthens the immune system, helping kids fight off illnesses more effectively.
Enhanced Cognitive Development
The new guidelines boost children’s cognitive development. Essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, iron, and zinc found in nutrient-dense foods support brain function and development. Research from the National Institutes of Health indicates that well-nourished children exhibit better concentration and cognitive skills. These nutrients improve memory and learning capabilities, positively influencing school performance and social interactions.
Long-term Healthy Habits
Following these guidelines establishes long-term healthy eating habits. When kids regularly consume nutritious meals, they develop a preference for healthy foods over processed options. Engaging children in meal planning and preparation makes them more likely to continue these practices into adulthood. Establishing these patterns early helps prevent chronic diseases later in life, ensuring sustained health and well-being.



 Editheena Kees – Health and Wellness Specialist Editheena Kees is a dedicated Health and Wellness Specialist at Makes Parenting Watch, where she combines her expertise in pediatric health, nutrition, and mental wellness to offer parents comprehensive support for raising healthy children. With a background in public health and family nutrition counseling, Editheena understands the importance of a balanced approach to both physical and mental well-being. She writes extensively on topics such as healthy eating habits for children, strategies for managing parental stress, and the importance of self-care for new parents. Editheena also emphasizes the significance of fostering healthy emotional development in children, offering tips on building resilience and maintaining strong family connections. Her holistic approach ensures that families are equipped not just to survive the challenges of parenting, but to thrive. In addition to her writing, Editheena collaborates with healthcare professionals to provide readers with the latest research and recommendations in child health.
Editheena Kees – Health and Wellness Specialist Editheena Kees is a dedicated Health and Wellness Specialist at Makes Parenting Watch, where she combines her expertise in pediatric health, nutrition, and mental wellness to offer parents comprehensive support for raising healthy children. With a background in public health and family nutrition counseling, Editheena understands the importance of a balanced approach to both physical and mental well-being. She writes extensively on topics such as healthy eating habits for children, strategies for managing parental stress, and the importance of self-care for new parents. Editheena also emphasizes the significance of fostering healthy emotional development in children, offering tips on building resilience and maintaining strong family connections. Her holistic approach ensures that families are equipped not just to survive the challenges of parenting, but to thrive. In addition to her writing, Editheena collaborates with healthcare professionals to provide readers with the latest research and recommendations in child health.